Plant Uses of Glucose
From the last section we saw that photosynthesis produces glucose and oxygen, using water and carbon dioxide and sunlight/chlorophyll in the process. What exactly does a plant use glucose for?
- Respiration - whenever we hear this word we automatically think of breathing, but respiration in plants, in fact in all living things is the process by which energy is transferred from glucose and this occurs in every cell. Respiration is an exothermic reaction, in other words it transfers energy out to the environment. There are two types of respiration but we will come to these later.
- Cellulose - glucose is converted into cellulose which is used to make strong cell walls, these strengthen and support the cells.
- Amino Acids - Also known as the building blocks of proteins, amino acids are produced when glucose is combined with nitrate ions absorbed from the soil through the roots of the plant.
Glucose itself is quite a soluble substance, and it's not ideal for plants to try to store it in this way.
Glucose is converted into starch and lipids which are easier for the plant to store. Lipids are also known as fats and oils and these can be stored in, for example, the seeds of plants such as sunflower seeds. Starch on the other hand is better to store because it is insoluble, the plant will store starch (for when there isn't much photosynthesis going on) as an energy reserve. starch is stored in the seeds and leaves of the plant as well as in the more obvious places such as the stems and roots. In fact potato tubers are starch stores.
|
|
|
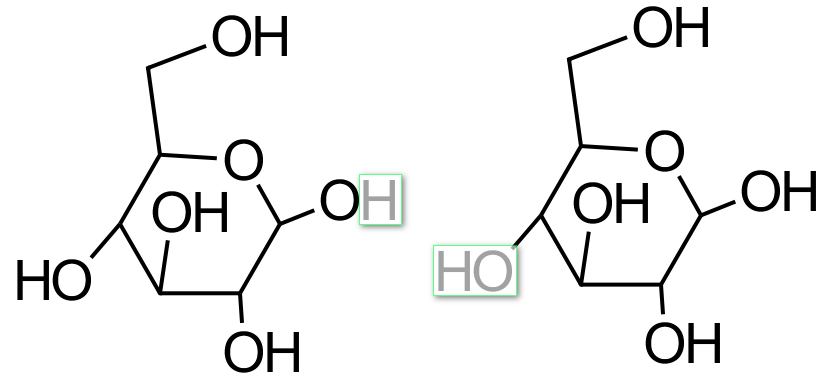
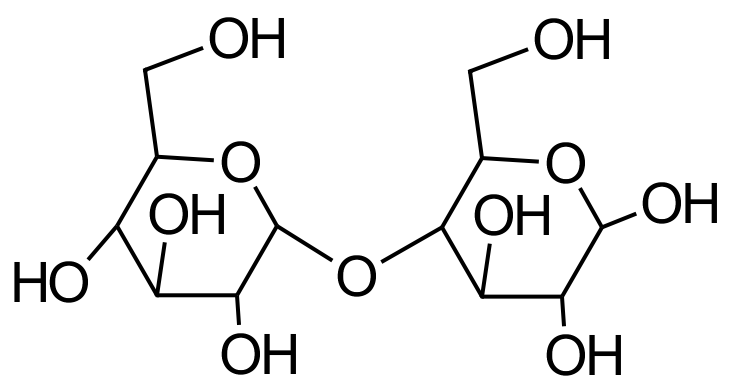
Two molecules of glucose approach each other as you see in the picture above. They join together to form the molecule shown in the picture below. The highlighted sections show a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl group coming away from the molecules to form H2O. This is known as a "condensation" reaction because it produces water. The molecule below is a simple starch, and further glucose molecules can add to it in the same way to make the chain of molecules even longer and turn it into a more complicated starch. This is how plants store excess glucose, utilising "carbohydrase" (an enzyme which reverses the process) to break the molecules back down into glucose when required. |
|
|
A simple experiment for you to try is to take a small piece of bread (white bread probably works better) and chew it, don't swallow it but just keep chewing and chewing and eventually you will start to experience a sweet taste. This is the carbohydrase in your saliva (amylase) breaking the starch in the bread back down into sugars.
Q. Give the name of the process the plants use to break down glucose so that the energy released can be used by the cells of the plant.
A. This process is known as respiration.
Q. What are the substances that the plant will absorb through its roots to combine with glucose to make substances called amino acids?
A. Nitrate ions (NO3-)
Q. What are amino acids used for?
A. Amino acids are used to make proteins.
Q. There are two ways in which glucose can be stored in plants for later use, one of them is the conversion into starch, name the other.
A. Conversion into lipids (fats and oils).
Q. Glucose is easier to store than starch because it is soluble, is this statement true or false?
A. This is false, glucose is soluble but this brings its own problems because dissolved glucose would cause the cells to swell. Starch is the method that plants prefer because of the fact that it is insoluble and therefore such problems will not happen.