The Nervous System
Organisms need to be able to respond to stimuli. There can be changes in the environment to which organisms may need to adapt to survive, for example if you were not able to feel pain you could be standing with your hand on a hot surface, being quite badly burnt and you would not know whether to respond to this or not. The nervous system gives you the ability to respond to your surroundings to remove or reduce injury or damage as a result of stimulus.
The nervous system is made up of neurones (nerve cells) in the body which are interconnected to detect, and where necessary respond to stimulus.
The nervous system is made up of several parts, receptors, neurones and effectors which detect stimuli (receptors), inform the brain of the detection (neurones) and receive messages containing instructions on how to respond (effectors).
Receptors - there are many types of receptors in the body, including:
Perhaps the most obvious receptor is our sense of touch.
When the receptors detect a form of stimulus, what happens next depends on the requisite response and is coordinated via the Central Nervous System. In vertebrate animals (animals with backbones) the Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord, additionally in mammals there is interconnection between sensory and motor neurones. All of these work together to detect stimulus and respond where needed.
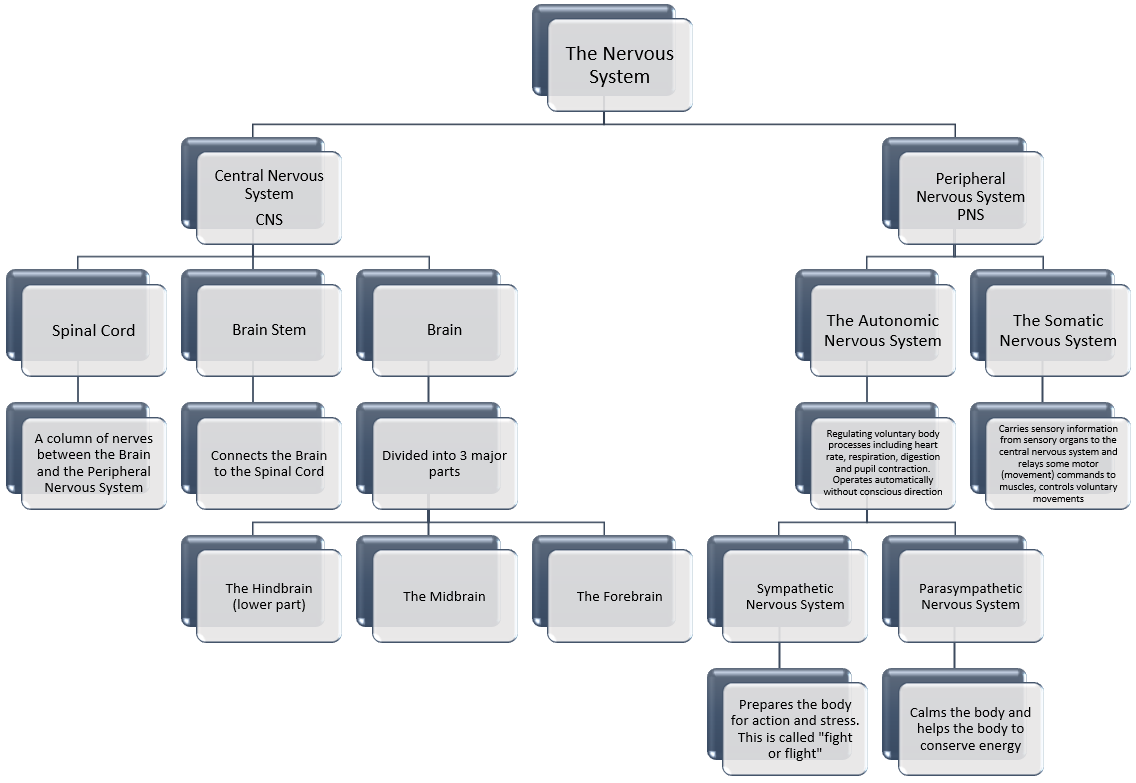
The above diagram shows quite a lot information, you need only concentrate for this particular topic on the Central Nervous System.
The whole cycle, between detection of the stimulus and the response to it is handled by the cooperation between the receptors, effectors, neurones and the responders.
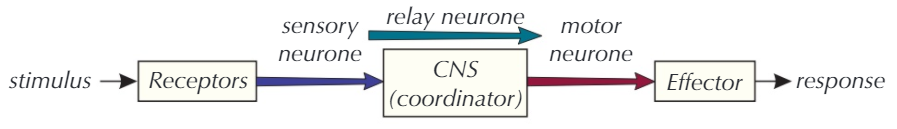
There are many types of receptor, and depending on the stimulus the choice of effector and what it does will be determined. Messages passed between receptors and effectors are controlled by the neurones. The neurones communicate with the central nervous system through the spinal cord.
There are 3 neurones to be aware of:
- Sensory Neurones which carry information as electrical impulses from the Receptors to the sense organs in the Central Nervous System.
- Relay Neurones which carry electrical impulses from the Sensory Neurones to the Motor Neurones these are found in the Central Nervous System.
- Motor Neurones which carry electrical impulses from the Central Nervous System to the Effectors.
So what exactly are the Effectors?. These are either muscles or glands, and respond to the nervous impulses received from the Motor Neurones. In the case of muscles, they will usually contract and in the case of glands they will usually secrete chemical substances called hormones.
Exercises:
Q1. Which type of effector secretes hormones?
A1. Consider the 2 types of effector, muscles and glands. Of course, only glands secrete hormones.
Q2. Name the 3 types of neurones, briefly explain what each one does
A2.
- Sensory Neurone - carries messages from the receptors to the CNS
- Relay Neurone - carries messages from the Sensory to the Motor Neurones
- Motor Neurone - carries messages from the CNS to the effectors
NB: in all cases the messages are carried as electrical impulses