[A] The Doppler Effect
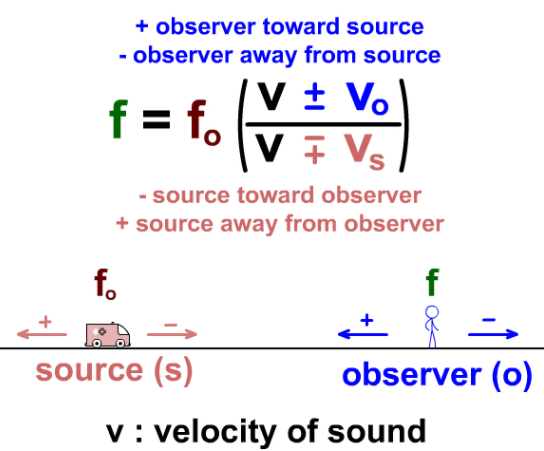
You may have noticed that when an ambulance or police car goes past, its siren is high-pitched as it comes towards you, and then becomes low-pitched as it goes away. This effect, where there is a change in frequency and wavelength, is called the Doppler effect. It happens with any wave source that moves relative to an observer.

The effect is as previously described. The approach of the source increases the frequency as the sound waves compress, this causes the observer to hear a sound which is apparently higher in frequency than it should be. At the point of coincidence, that is when the source and observer are together, the frequency produces a sound as it should be. As the source passes and moves into the distance, away from the observer, the frequency reduces as the sound waves "stretch out".
Calculation of the perceived frequency is not difficult if the speed of sound in air is known, and the relative speeds of the source and observer together with frequency data.
>> Questions <<