Red Shift
Light from a star does not contain all the wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. Elements in the star absorb some of the emitted wavelengths, so dark lines are present when the spectrum is analysed.
Different elements produce different patterns of dark lines.
The diagram below shows part of the emission spectrum of light from the Sun:
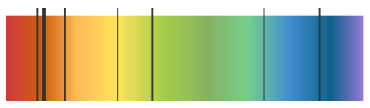
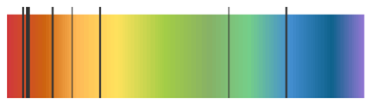
Astronomers can observe light from distant galaxies. When they do this, they see it is different to the light from the Sun. The dark lines in the spectra from distant galaxies (below) show an increase in wavelength.
The lines are moved or shifted towards the red end of the spectrum.
This effect is called red-shift.
The diagram shows part of the emission spectrum of light from a distant galaxy:
But what is "Red Shift" ?
Consider the following image of a transverse wave:
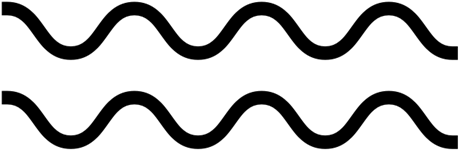
In this picture we can see that the wavelength is the distance between peaks, troughs or centre points, in other words one complete cycle of the wave. If the light source is moving towards us, the waves are "compressed" as if they are being pushed back as shown. In this case the wavelength decreases, and the colour of light shifts towards the blue end of the spectrum. This is called a "blue shift"...............
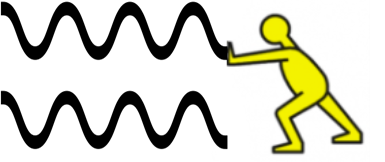
If the light source is travelling away from us, the waves are stretched (lengthened) which causes them to move towards the red end of the spectrum. This is known as a "red shift".

Scientists have observed that the light from most distant galaxies is red shifted, which suggests that they are moving away from us. This suggests to us that the universe is constantly expanding and supports the "Big Bang Theory" more so than the "Steady-State Theory". There are some unexplained theories, scientists are of the opinion that the universe is made up of "dark matter" and "dark energy", In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is hypothetical matter that is undetectable by its emitted radiation, but whose presence can be inferred from gravitational effects on visible matter.