Carbonates
At this level the number of anions that you will be expected to know the tests for is limited. You will need to know the test for Carbonates, Sulphates and the Halides.
The standard test for Carbonates is to introduce a sample to a dilute acid, gaseous Carbon Dioxide will be released and you will also have a salt and water. This is an example of what is known as a "double displacement" (or previously, a "double decomposition") reaction:

Although it seems to be rarely shown now, this reaction would involve the exchange of Chloride and Carbonate to produce Calcium Chloride and Carbonic acid, however carbonic acid dissociates readily into its components Water and Carbon Dioxide:

Evolution of the gas is the first part of the test, we need to identify the gas given off and we do this by bubbling it through "lime water" which is a dilute solution of Calcium Hydroxide in water. The aqueous solution of Calcium Hydroxide reacts with the Carbon Dioxide bubbled through it to produce a milky solution of Calcium Carbonate and water.

However, continued bubbling of Carbon Dioxide through this solution will clear it as soluble Calcium Hydrogen Carbonate begins to form:
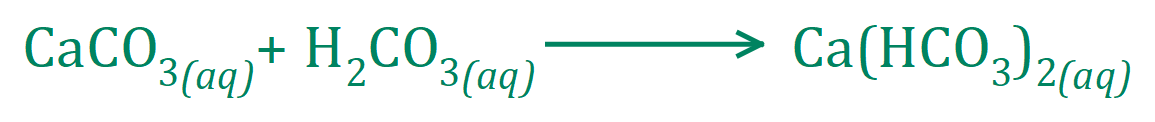
There is a lot of chemistry in this simple, basic test for a Carbonate !