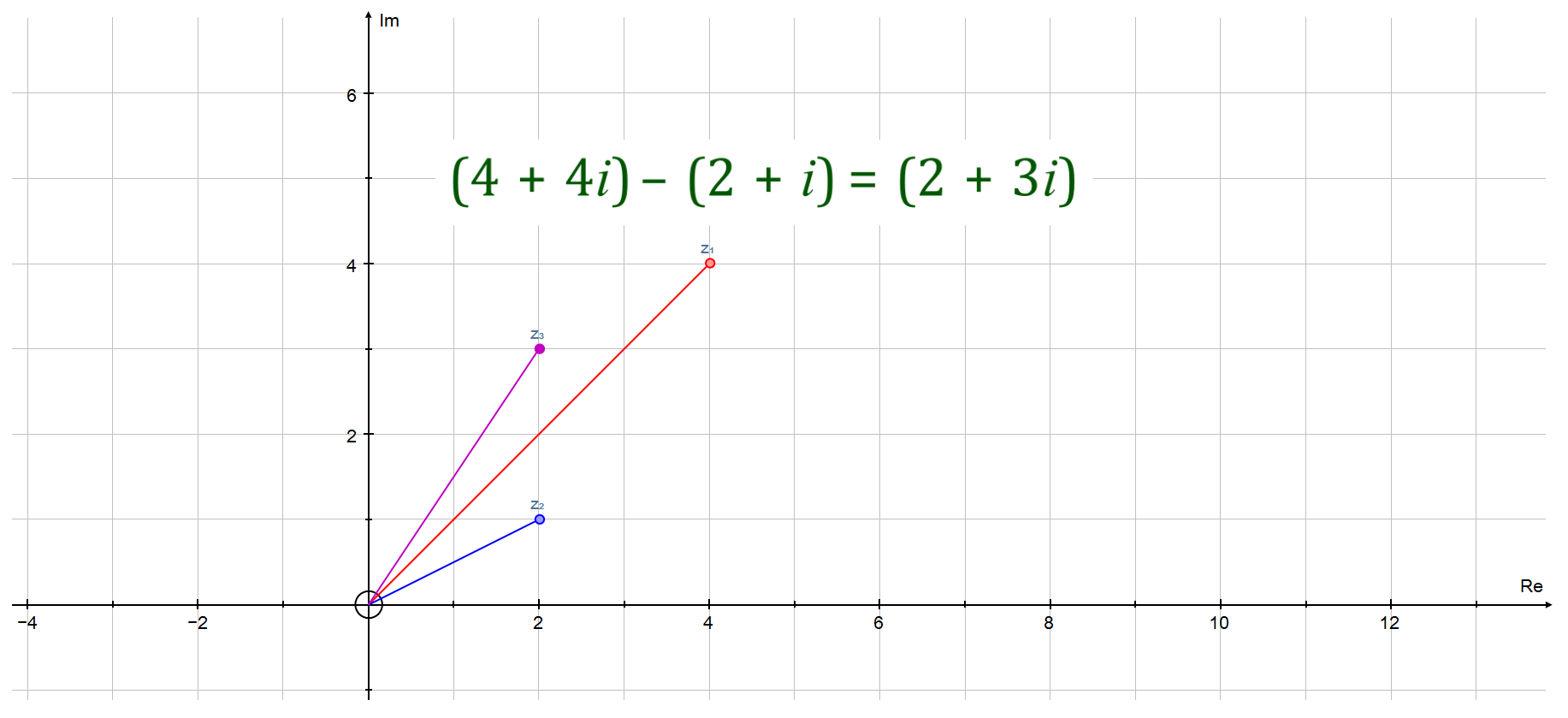
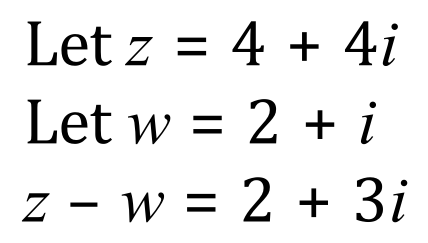[A] The Complex Plane - Argand Diagrams
Earlier in this book, we considered numbers to lie on a one-dimensional line starting from the unit zero and extending in two directions to represent positive numbers to infinity (right) and negative numbers to infinity (left).
We now ask ourselves "is there any way we can display complex numbers diagrammatically in the same way as we do "real" numbers?". We can do this in two dimensions using an "Argand Diagram". Plotting a complex addition or a complex subtraction will produce points in two dimensions which link to form a parallelogram.
The image here is the "general" idea of a "two dimensional number line" using this method:
Argand Example 1:
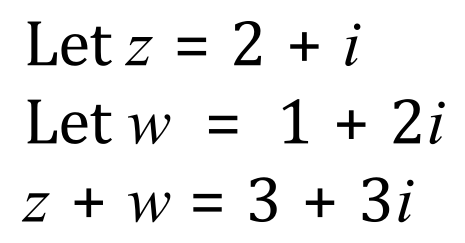
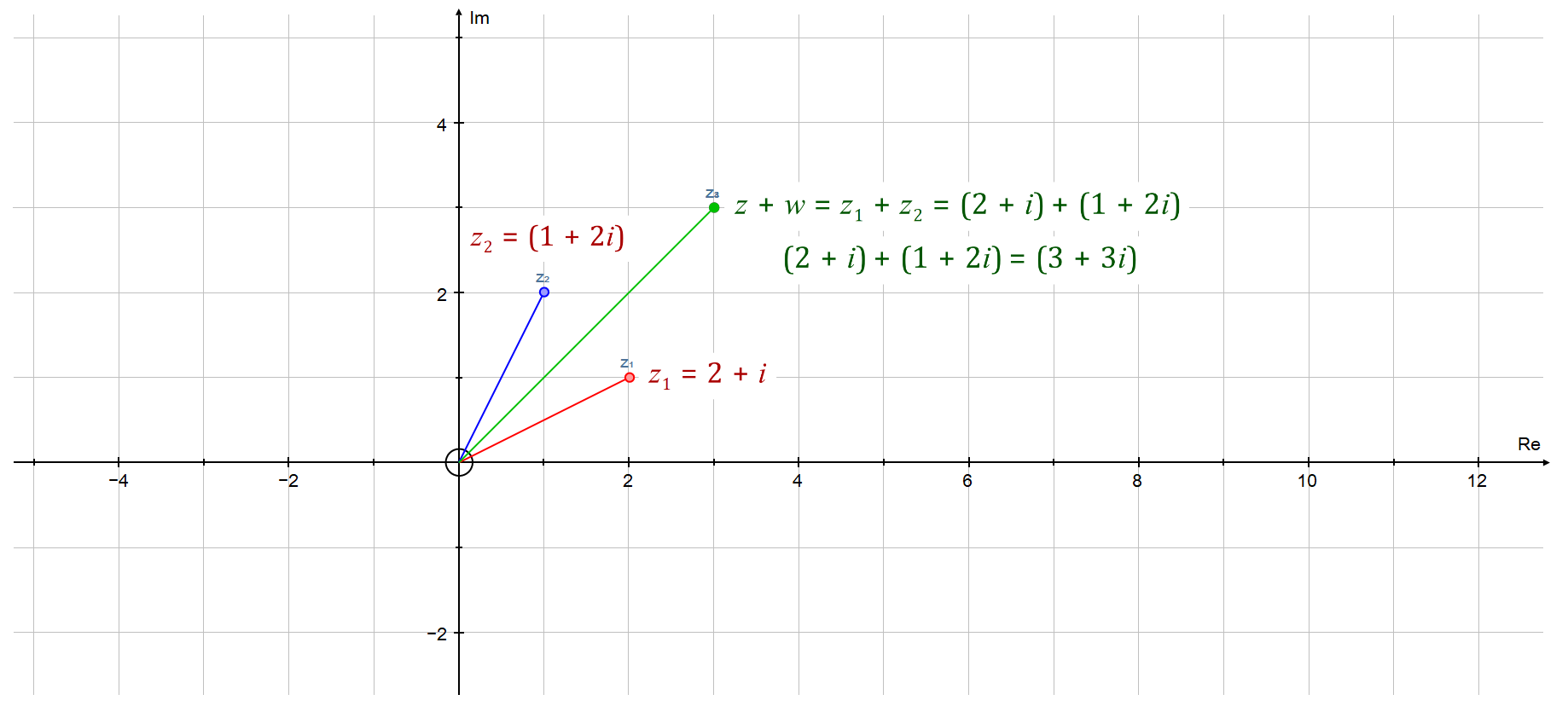
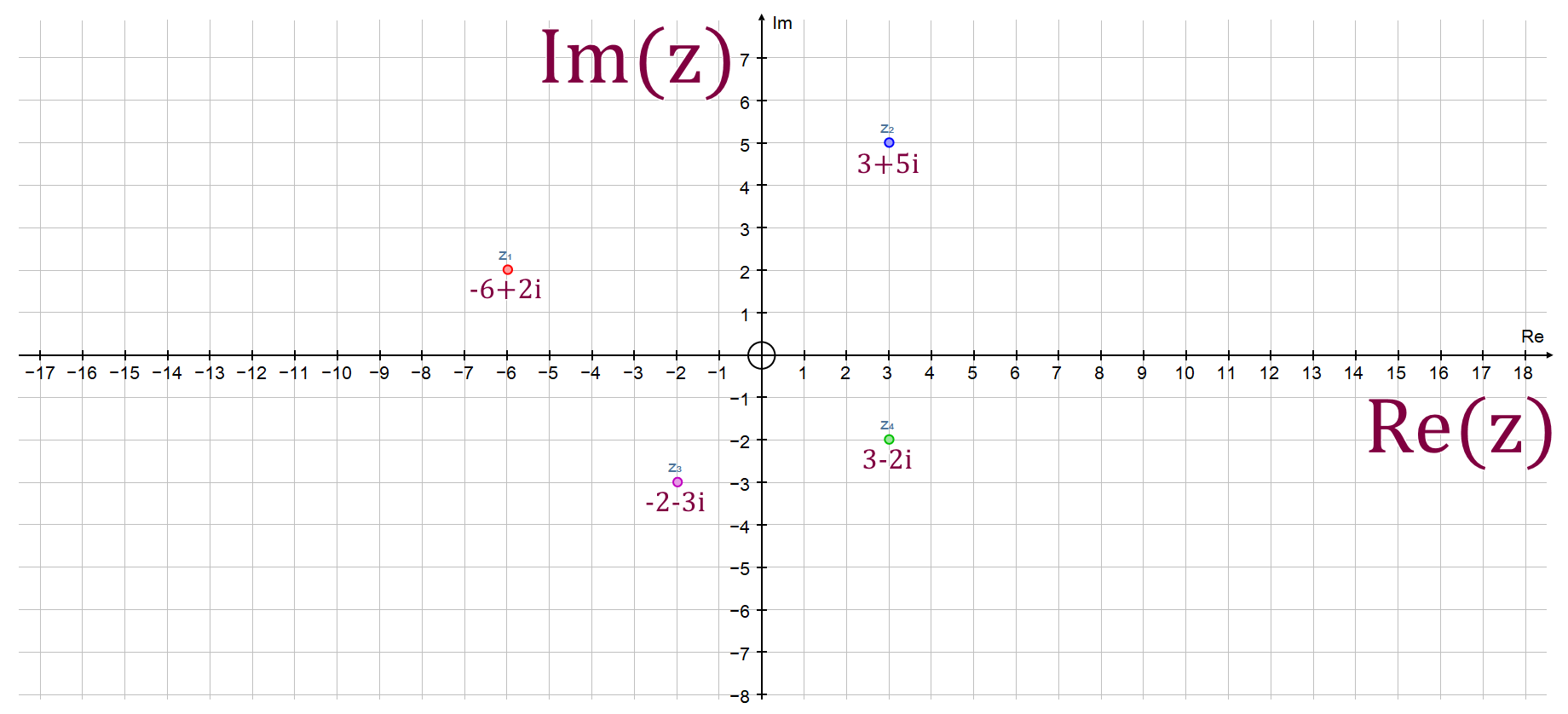
Argand Example 2: