Alpha Decay
Alpha particles, essentially helium nuclei, rejected from the nucleus during alpha decay. When an unstable nucleus loses an alpha particle, it loses 2 neutrons and 2 protons, an essentially double positive unit which reduces the atomic number by 2 and the mass number by 4 of the parent nucleus.
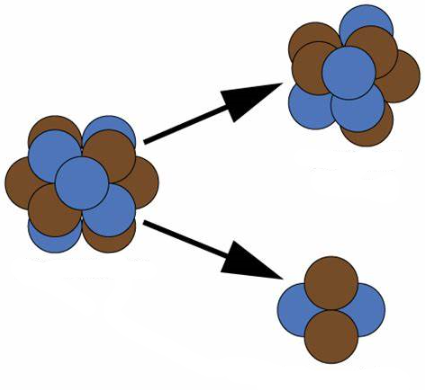
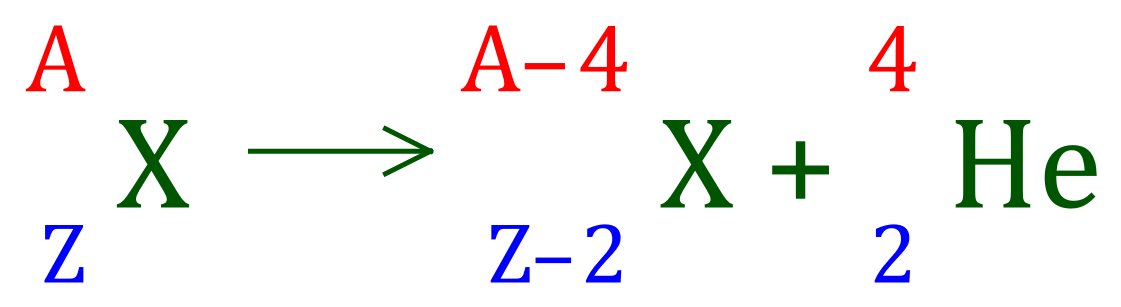
Examples:
Alpha Decay - Uranium to Thorium
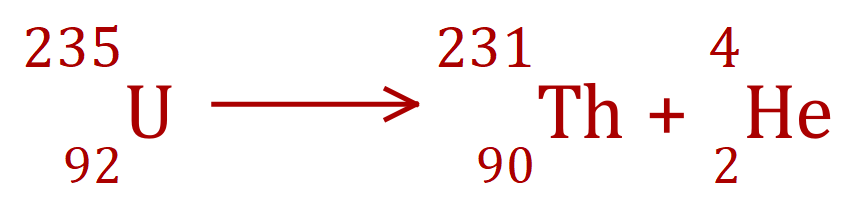
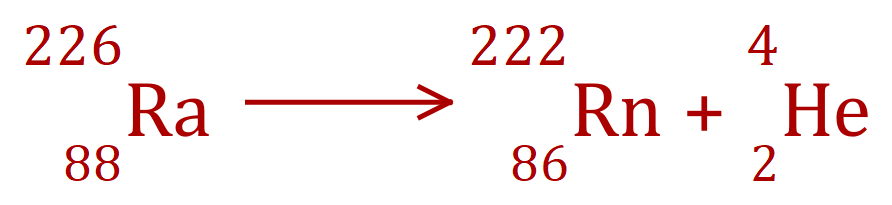
Alpha Decay - Radium to Radon
Alpha Decay - Radon to Polonium
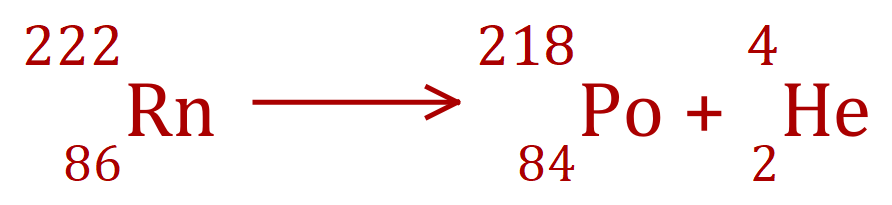
The arithmetic is very simple in alpha decay, loss of an alpha particle removes 4 from the mass number, and 2 from the atomic number. This naturally results in the conversion of one element to another.
>> Questions <<
Go To >> Radioactive Decay Pathways <<