Charles Law
Charles law states that a fixed mass of gas held a constant pressure will have a volume which is directly proportional to the temperature applied:
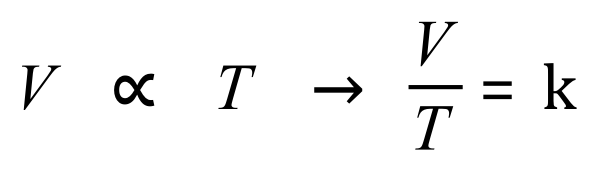
This law exemplifies the physical properties of gases, in that gases expand when heated. It can be particularly useful to show increases or decreases in volume when temperature is varied, and vice versa.
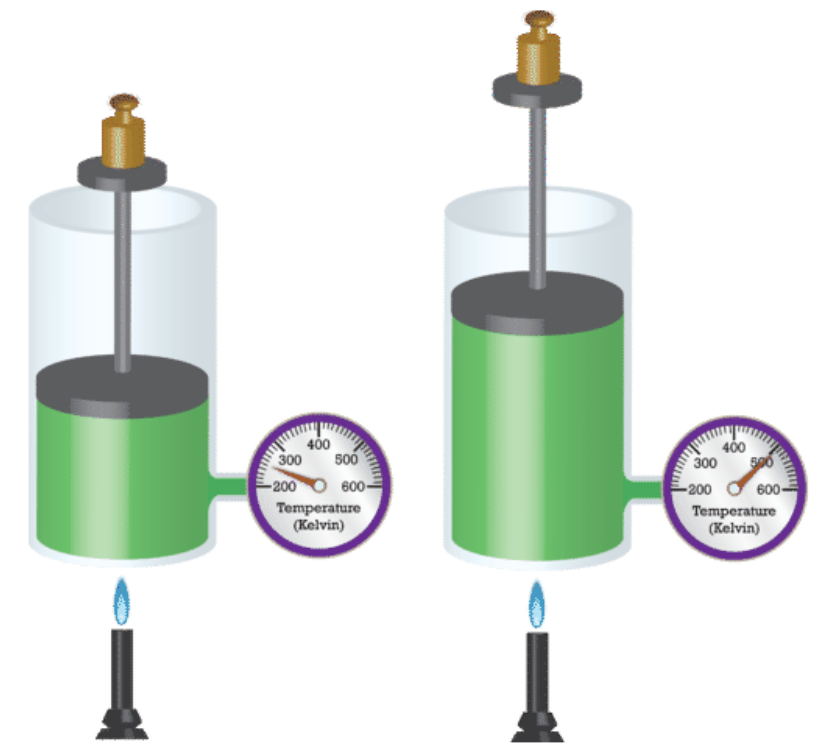
Q. 2 cubic metres of a certain gas are held at 300 K. The temperature of the gas is increased to 450 K. What is the new volume of the gas at this increased temperature?
A. Given the fact that:
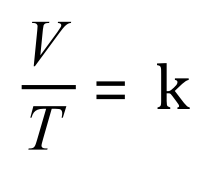
We can say that:

Inserting our known values for V1, T2 and T1:
