Electrolysis In Aqueous Solution
Q. An electrolysis setup is created and an electrical current is passed through a dilute solution of aqueous Potassium Iodide.
- State the product that will be produced at the cathode.
The ions present in solution will be potassium cations, hydroxonium cations, iodide anions and hydroxide anions. Looking at the reactivity series of metals we can see the potassium is far more reactive than hydrogen, therefore the hydroxonium cations will be reduced at the cathode to water and hydrogen gas.
- State the product that will be produced at the anode.
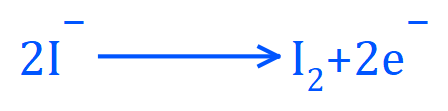
The positively charged anode will attract the negatively charged hydroxide ions and iodide ions. As there is a halogen in solution, it will be liberated first, therefore iodide anions will be oxidised to iodine atoms at the anode. These will form iodine molecules in solution.
- Write out the half equation for the reaction taking place at the cathode.

- Write out the half equation for the reaction taking place at the anode.
Q. Water is a poor conductor of electricity. Although it does contain some Hydrogen ions H+ / H3O+ and some Hydroxide ions OH- due to a small amount of dissociation, water can be made into a slightly better conductor if it is slightly acidified with, say for example dilute Sulphuric Acid. Predict the electrolysis products when an electric current is passed through acidified water. Write out the half equation is taking place at each electrode and the full balanced equation for the reaction.
Let's start first of all by taking a look at the ions that we have in solution:

From this we should be able to establish that the positive electrode (the anode) will attract the negative Hydroxide ions. At the anode these ions will be oxidised to water and Oxygen gas:
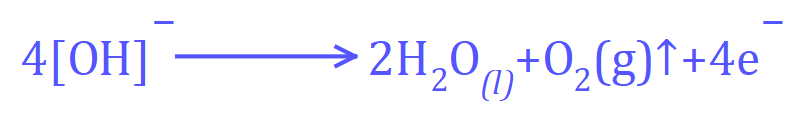
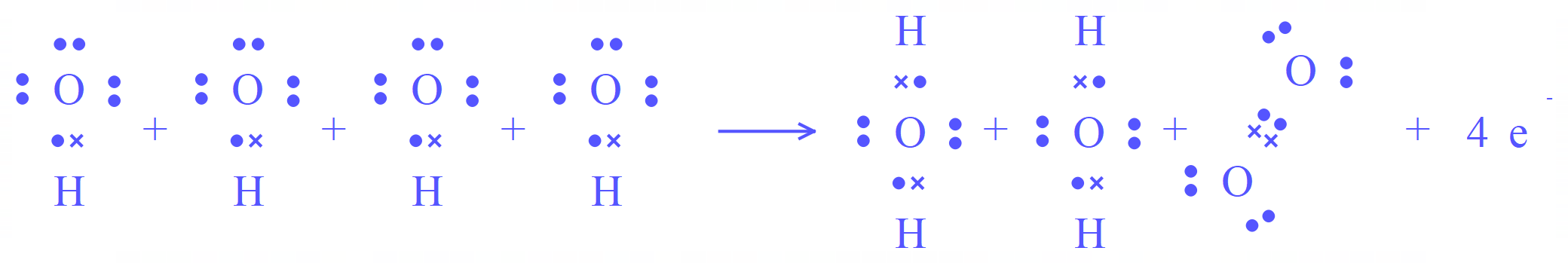
Conversely at the negative electrode (the cathode) the following reaction will take place:
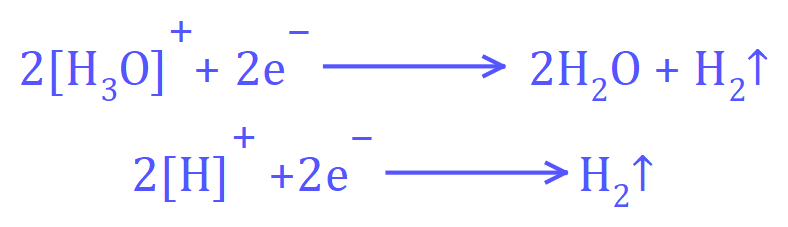
Either of these representations would be acceptable, the reduction of the Hydroxonium ion to water and Hydrogen gas or the reduction of protons to Hydrogen gas.
The overall reaction for the electrolysis of water is as follows:
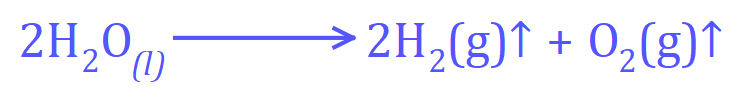
Q. If a solution of aqueous Copper Nitrate is electrolysed, what would be the electrolysis products? Write the half equations occurring at both electrodes.
In this particular electrolysis, The products of the electrolysis will be Copper metal deposited on the cathode and Oxygen gas liberated at the anode. How we establish this first of all requires us to know the identities of the ions present in the solution. So, what ions are there in this solution? - Cu2+ NO3- H3O+ and OH- . Now that you have an idea of what ions are there, which ones will migrate towards the positive (anode) and which will migrate towards the negative (cathode) ?
Positive Copper ions will migrate towards the negative electrode (the cathode) and Hydroxide ions will migrate towards the anode.
At the anode:
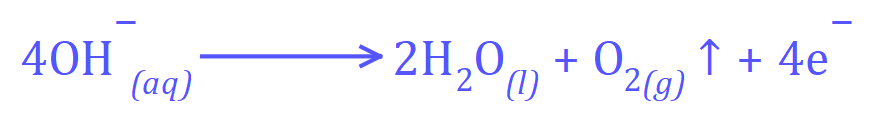
At the cathode:
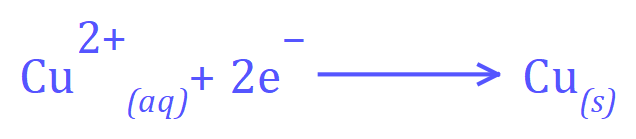
Q. What difference, if any, would there be to the products of the electrolysis above if Copper Nitrate was swapped for Potassium Nitrate?
The answer to this question actually hinges on your understanding of the reactivity series. If you take a look at the reactivity series of metals you will see that potassium is in fact at the top, therefore there will be a change in product at the cathode:
At the anode (positive):
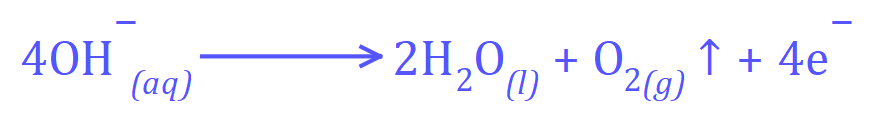
At the cathode (negative):

So, exchanging Copper Nitrate for Potassium Nitrate will lead to the production of Hydrogen gas as opposed to the metallic element, as Potassium is far more reactive than Hydrogen it will remain in solution.
Go To >> Questions <<
Back To >> Electrolysis In Aqueous Solution <<