Eukaryotes and Subcellular Structures
A typical animal cell (eukaryote):
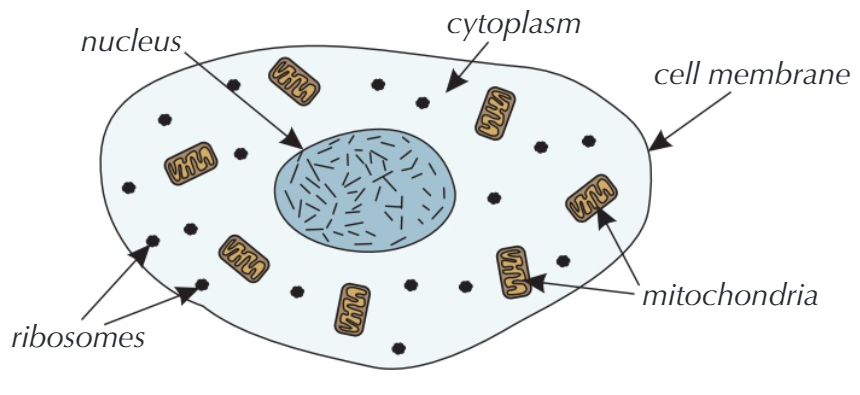
The above diagram shows a typical animal cell which is eukaryotic, and the subcellular structures are described thus:
|
Nucleus |
The nucleus contains all of the genetic material which controls the activities of the cell. |
|
Cytoplasm |
The cytoplasm is a gel -like substance where most of the chemical reactions take place, and contains enzymes which control these reactions. |
|
Cell Membrane |
The cell membrane holds the cell together, and controls what enters and what leaves the cell. |
|
Mitochondria |
These are where most of the reactions for aerobic respiration take place, respiration transfers energy which the cells need to work. |
|
Ribosomes |
These are where proteins are made in the cell. |
A plant cell, also eukaryotic, has all of the structures of the animal cell, PLUS a few more:
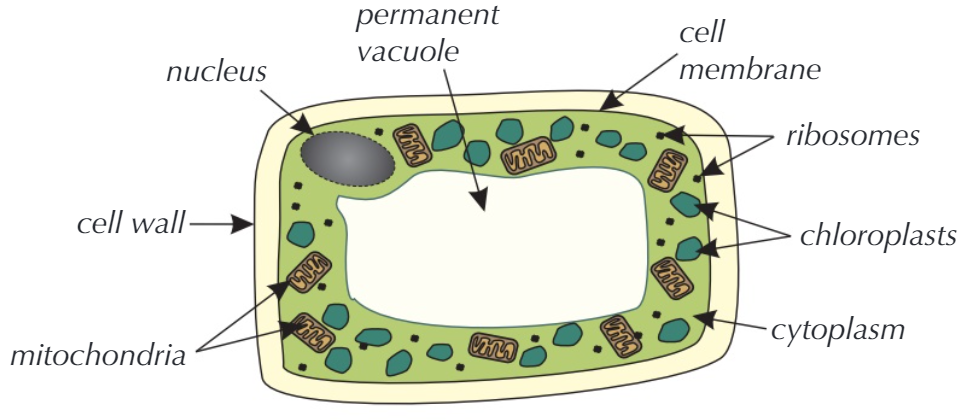
|
Cell Wall |
A rigid structure made of cellulose, this gives the cell physical strength / rigidity. |
|
Permanent Vacuole |
Contains a weak solution of sugar and salts, known as Cell Sap |
|
Chloroplasts |
These are where photosynthesis occurs, holding a green substance called chlorophyll which absorbs sunlight. |