Sine Rule
The SINE Rule
In any triangle when we consider the internal angles ‘a’ ‘b’ and ‘c’ and the sides ‘A’ ‘B’ and ‘C’ the sine rule states:
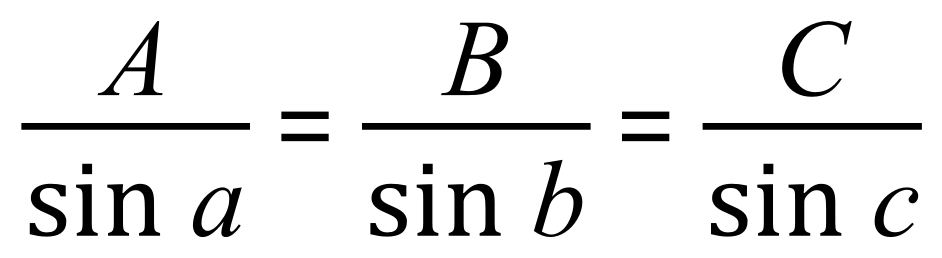
Or of course the inverse of this:
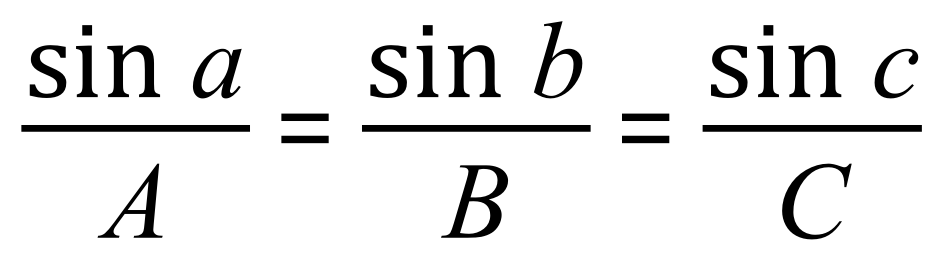
We can use the sine rule if we have either:
- Two sides and a known angle opposite either of them, or
- Two angles and any side.
Let’s have a look at an example:
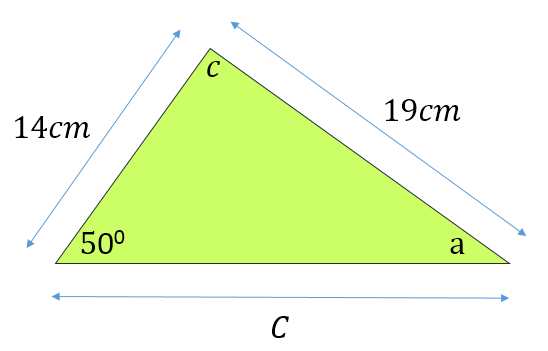
From this diagram we can see that we know:
Angle ‘b’ = 500
Side B = 19cm
Side A = 14cm
We have two sides and one opposing angle so the sine rule can be used.
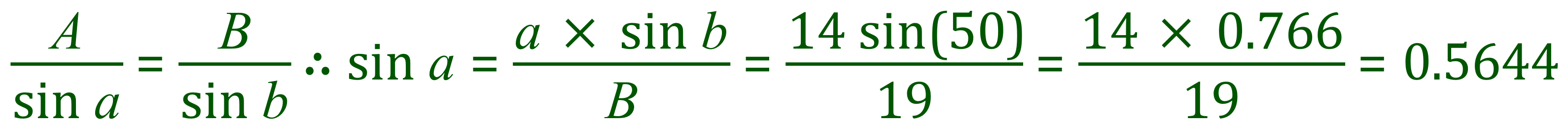
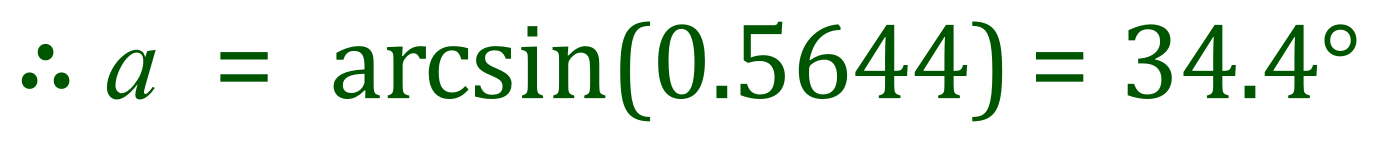
Now that we have two angles, we can add them together and subtract the result from 1800 to find the remaining angle:
![]()
Using the sine rule again, we can establish that the length of the remaining side C is thus:
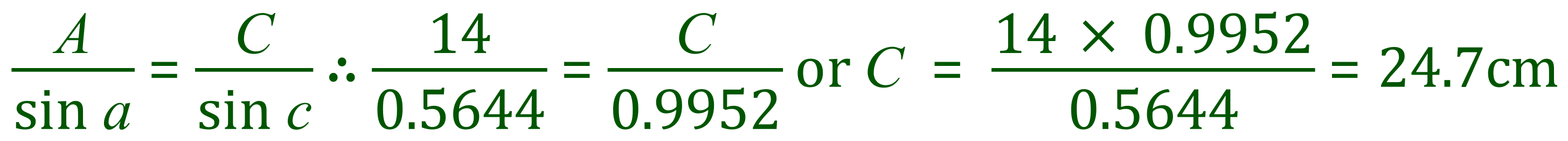
Sine Rule >> Questions <<