The Thermite Reaction
A thermite reaction is one between a (less reactive) metal oxide and another (more reactive) metal, typically iron oxide and aluminium. Put simply the more reactive metal ‘steals’ the oxygen from the other oxide, releasing a significant amount of heat.
Performed in a laboratory such as at school, the mixture of Iron(III) Oxide and powdered Aluminium is mixed in a crucible, with a strip of Magnesium metal acting as a fuse. The Magnesium is ignited with a strong flame (do NOT look at the burning magnesium) and the mixture ignites.


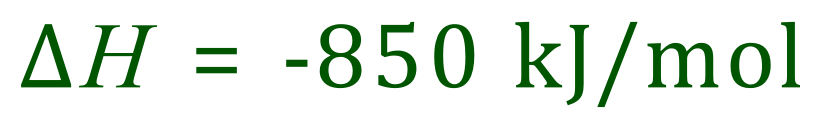
Go To >> Appendix C3 - Reactivity Series Of Metals <<