Bond Breaking and Bond Formation
Calculate the energy requirements in the following scenarios.
Q1. Calculate the energy needed to break all of the bonds in 1 mole of Methane.
A1. Methane is:
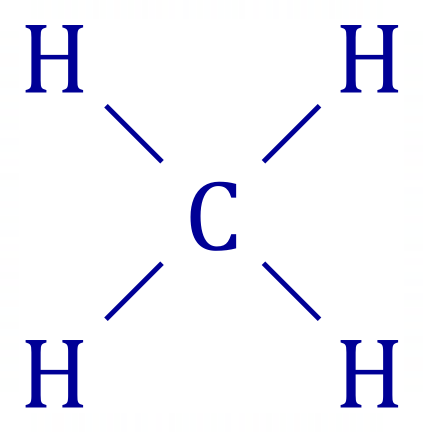
The bond energy (enthalpy) of the C-H bond in this case is 413 kJ mol-1 and each molecule has 4 such bonds. The total MOLAR energy required would therefore be:
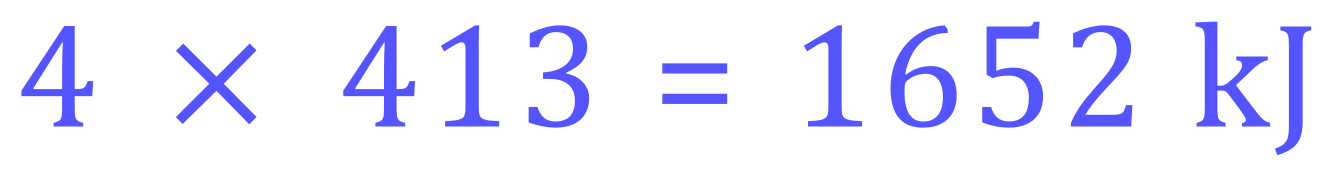
Q2. Calculate the energy needed to break all of the bonds in 2 moles of Ethane.
A2. Ethane is:
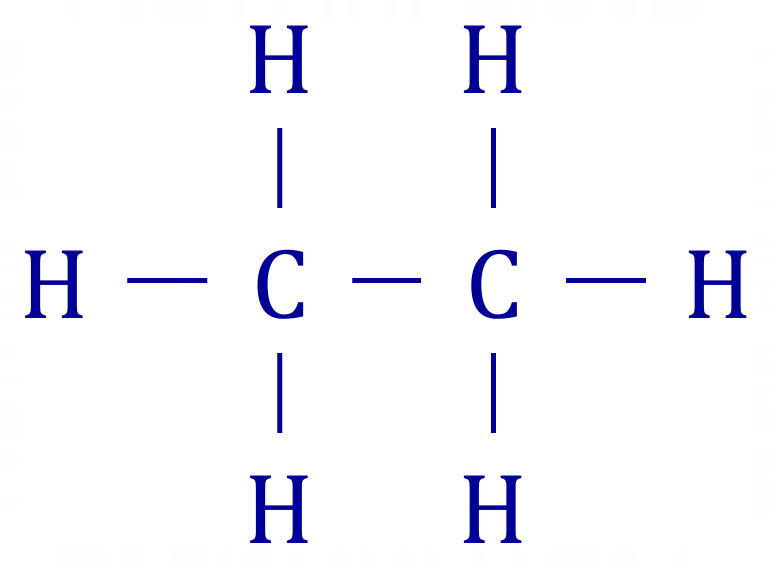
Therefore we have 1 x C-C single bond and 6 x C-H single bonds.
C-C = 347 kJmol-1
C-H = 413 kJmol-1
The MOLAR energy would therefore be:
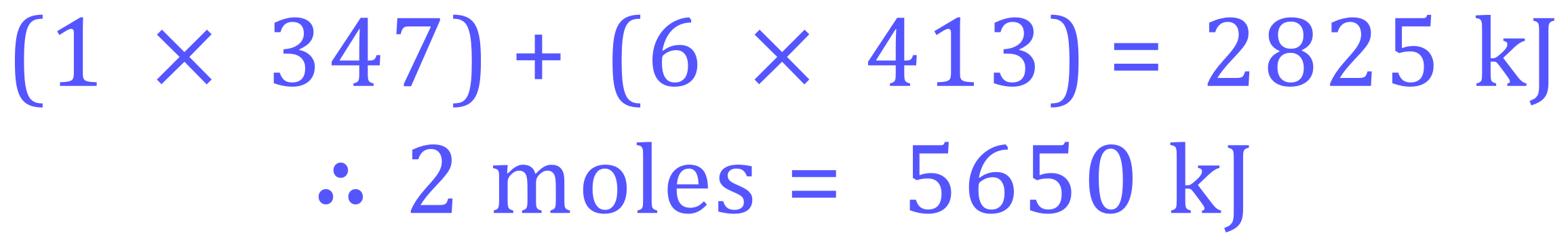
Q3. Calculate the energy needed to break all of the bonds in 1 mole of Ethyl Ethanoate.
A3 Ethyl Ethanoate (Ethyl Acetate) is an ester produced by reacting Ethanoic Acid with Ethanol, and has this displayed formula:
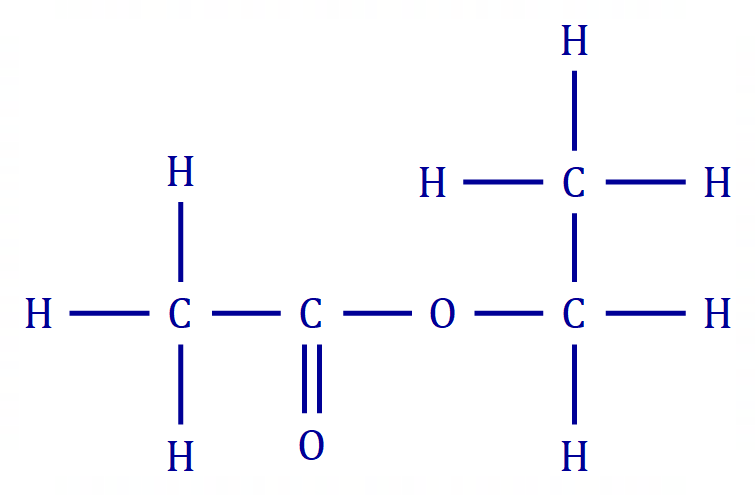
When the molecules start to become a little unwieldy it is best to make a small table of the bonds present, and their numbers and energies:
|
C-H |
8 |
413 kJmol-1 |
|
C-C |
2 |
347 kJmol-1 |
|
C-O |
2 |
358 kJmol-1 |
|
C=O |
1 |
745 kJmol-1 |
The calculation can now be completed by multiplying the respective bond energies by the number of instances of each, and then add them up.
![]()
Back To >> Questions <<
Back To >> Bond Breaking and Bond Formation <<
Go To >> Appendix C5 - Selected Bond Energies <<